两种标签
Spring中的标签的包括默认的标签和自定义的标签两种,而这两种标签的用法和解析方式存在着很大的不同。
默认标签的解析
默认标签的解析是在parseDefaultElement函数中进行的,函数中的功能逻辑一目了然,分别对4种不同的标签做了不同的处理:
- import
- alias
- bean
- beans
bean标签的解析以及注册
在4种标签的解析中,对bean的解析最为复杂也最为重要。因此由此深入,如果将此标签的解析过程理解了,其他标签的解析自然也会迎刃而解。
processBeanDefinition(ele,delegate)
/**
* Process the given bean element, parsing the bean definition
* and registering it with the registry.
*/
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
- 首先委托BeanDefinitionDelegate类的parseBeanDefinitionElement方法进行元素解析,返回BeanDefinitionHolder类型的实例bdHolder。在这个方法之后,bdHolder实例已经包含了我们配置中的各种属性了,例如class、name、id、alias之类的属性了。
- 当返回的bdHolder不为空的情况下,如果存在默认标签下的子节点下再有自定义属性,还需要在此对自定义标签进行解析。
- 解析完成后,需要对解析后的bdHolder进行注册,同样,注册操作委托给了BeanDefinitionReaderUtils的registerBeanDefinition方法。
- 最后发出响应时间,通知相关的监听器,在这个时候,这个bean已经加载完成了。
解析BeanDefinition
/**
* Parses the supplied {@code <bean>} element. May return {@code null}
* if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}.
*/
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele) {
return parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, null);
}
/**
* Parses the supplied {@code <bean>} element. May return {@code null}
* if there were errors during parse. Errors are reported to the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ProblemReporter}.
*/
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//解析id的属性
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
//解析name的属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
//分割name的属性
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
//对标签中其他属性的解析过程
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
//如果bean没有beanName,就使用默认方法生成beanName
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
在当前层,完成的主要工作如下:
- 1.提取了元素中的id和name属性
- 2.进一步解析其他所有属性并封装至AbstractBeanDefinition类型的实例中
- 3.如果检测到bean没有指定beanName,那么使用默认的规则为此Bean生成BeanName
- 4.将获取到的信息封装到BeanDefinitionHolder的实例中
接下来我们接着来看一下步骤2中的对标签其他属性的解析过程:
/**
* Parse the bean definition itself, without regard to name or aliases. May return
* {@code null} if problems occurred during the parsing of the bean definition.
*/
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
//解析class属性
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
//解析parent属性
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
//使用className和parent创建一个用于承载各种属性的AbstractBeanDefinition实例 bd
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//硬编码解析默认bean的各种属性
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
//提取description
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//解析元数据
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
//解析lookup-method属性
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析replace-method属性
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析构造函数参数
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//解析property子元素
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
//解析qualified子元素
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
bean标签的所有属性,不论是常用的还是不常用的我们都按到了,尽管有些复杂的属性需要进一步解析。接下来主要就是看一些复杂标签属性的解析。
创建用于属性承载的BeanDefinition(CreateBeanDefinition)
BeanDefinition是一个接口,在Spring中存在三种实现:RootBeanDefinition,ChildBeanDefinition,GenericBeanDefinition。三种实现方式均集成了AbstractBeanDefinition,其中BeanDefinition是配置文件元素标签的内部表示形式。(元素标签拥有class、scope、lazy-init等配置属性,而BeanDefinition咋提供了相应的beanClass、scope、LazyInit属性,BeanDefinition和中的属性是一一对应的。其中RootBeanDefinition是最常用的实现类)。
在配置文件中可以定义父和子,父使用RootBeanDefinition来表示,子使用ChildBeanDefinition来表示,而没有父的就用RootBeanDefinition来表示。AbstractBeanDefinition对两者共同的类信息进行抽象。
Spring通过BeanDefinition将配置文件中的配置信息转化为容器的内部表示,然后将这些BeanDefinition注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry当中。
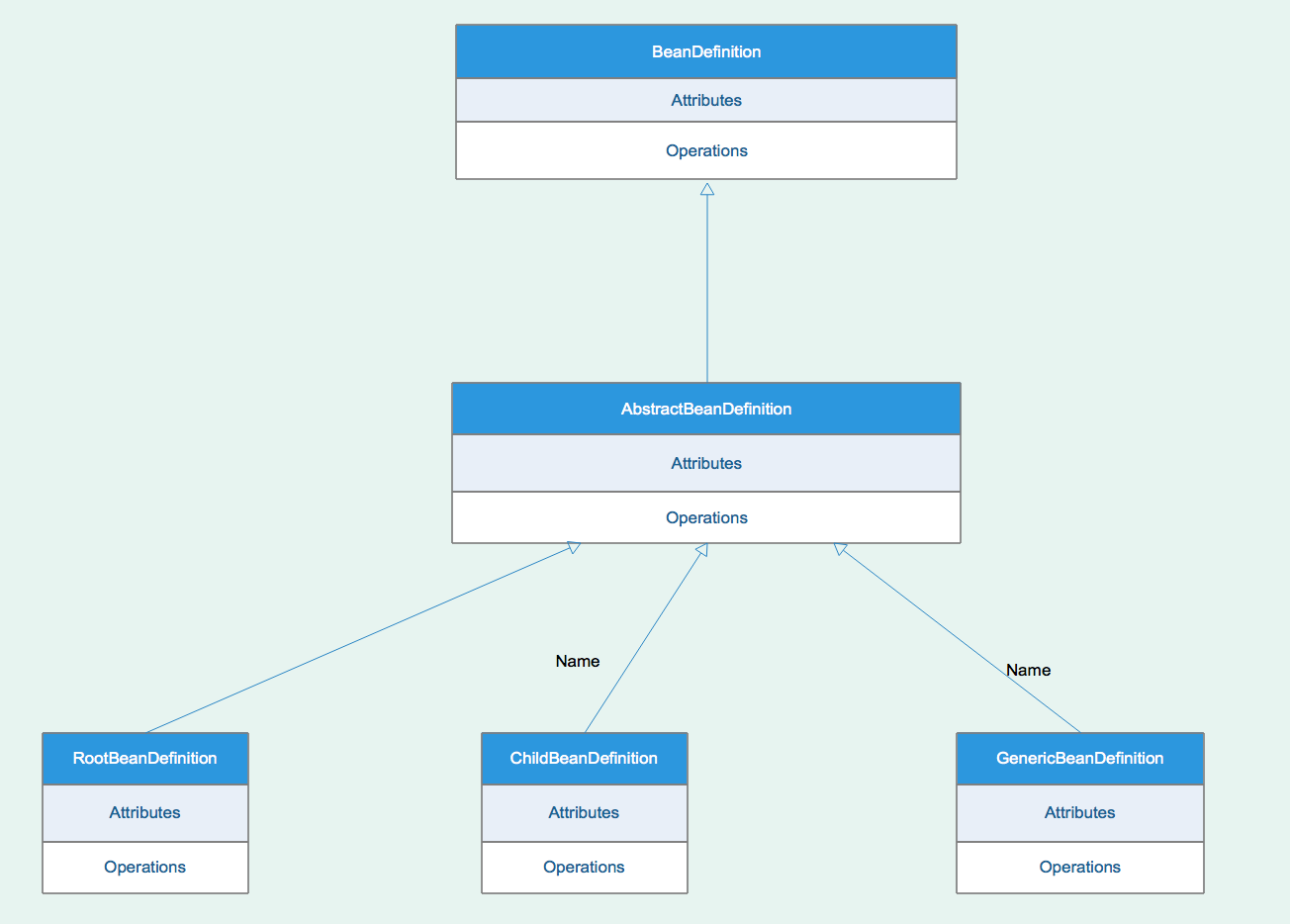
要解析属性,首先要创建用于承载属性的实例,也就是创建GenericBeanDefinition类型的实例,而 AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);就是实现这个功能
/**
* Create a new GenericBeanDefinition for the given parent name and class name,
* eagerly loading the bean class if a ClassLoader has been specified.
* @param parentName the name of the parent bean, if any
* @param className the name of the bean class, if any
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading bean classes
* (can be {@code null} to just register bean classes by name)
* @return the bean definition
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the bean class could not be loaded
*/
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
//如果classLoader不为空,则使用以传入的classLoader同一虚拟机加载类对象,否则只是记录ClassName
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
解析各种属性(parseBeanDefinitionAttributes方法)
在上一步,创建了Bean信息的承载实例字后,就可以进行bean信息的各种属性的解析了。我们进入到parseBeanDefinitionAttributes方法。
/**
* Apply the attributes of the given bean element to the given bean * definition.
* @param ele bean declaration element
* @param beanName bean name
* @param containingBean containing bean definition
* @return a bean definition initialized according to the bean element attributes
*/
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(Element ele, String beanName,
@Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) {
//判断是否是单例的属性,如果有的话需要报错
if (ele.hasAttribute(SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
error("Old 1.x 'singleton' attribute in use - upgrade to 'scope' declaration", ele);
}
//解析scope属性
else if (ele.hasAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setScope(ele.getAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (containingBean != null) {
// Take default from containing bean in case of an inner bean definition.
//如果在嵌入beanDefinition情况下且没有单独制定scope属性的时候则使用父类默认的属性
bd.setScope(containingBean.getScope());
}
//解析Abstract属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setAbstract(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//解析lazy-Init属性
String lazyInit = ele.getAttribute(LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(lazyInit)) {
lazyInit = this.defaults.getLazyInit();
}
bd.setLazyInit(TRUE_VALUE.equals(lazyInit));
//解析autowire属性
String autowire = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setAutowireMode(getAutowireMode(autowire));
//解析depend-on的属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String dependsOn = ele.getAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDependsOn(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(dependsOn, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS));
}
//解析autowireCandidate属性
String autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ("".equals(autowireCandidate) || DEFAULT_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate)) {
String candidatePattern = this.defaults.getAutowireCandidates();
if (candidatePattern != null) {
String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(candidatePattern);
bd.setAutowireCandidate(PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(patterns, beanName));
}
}
else {
bd.setAutowireCandidate(TRUE_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate));
}
//解析primary属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setPrimary(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//解析init-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String initMethodName = ele.getAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getInitMethod() != null) {
bd.setInitMethodName(this.defaults.getInitMethod());
bd.setEnforceInitMethod(false);
}
//解析destroy-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getDestroyMethod() != null) {
bd.setDestroyMethodName(this.defaults.getDestroyMethod());
bd.setEnforceDestroyMethod(false);
}
//解析factory-method属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryMethodName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
//解析factory-bean属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryBeanName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE));
}
return bd;
}
我们可以看到,这个方法完成了对所有bean属性的解析。
解析子元素meta
meta属性的使用
<bean id="myTestBean" class="bean.myTestBean">
<meta key = "testStr" value = "aaaaaaaaa">
</bean>
这段代码并不会体现在MyTestBean的属性当中,而是一个额外的声明,当需要使用里面的信息的时候可以通过BeanDefinition的getAttribute(key)的方法获取
对meta属性的解析代码如下
public void parseMetaElements(Element ele, BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor attributeAccessor) {
//获取当前节点
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
//提取meta
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
Element metaElement = (Element) node;
String key = metaElement.getAttribute(KEY_ATTRIBUTE);
String value = metaElement.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
//使用key和value构造BeanMetadataAttribute
BeanMetadataAttribute attribute = new BeanMetadataAttribute(key, value);
attribute.setSource(extractSource(metaElement));
//记录信息
attributeAccessor.addMetadataAttribute(attribute);
}
}
}
解析子元素lookup-method
这个属性不是很常用,通常称这个为获取器注入。(P44)
解析子元素replaced-method
方法替换:可以在运行时用新的方法替换现有的方法。replaced-method不但可以动态返回实体bean,而且还能动态地更改原有方法的逻辑。(P46)
解析子元素constructor-arg
对构造函数进行的解析(P48)
解析子元素property
p53
解析子元素qualifier
p54
AbstractBeanDefinition属性
至此完成了XML文档到GenericBeanDefinition的转换。但是Generic只是子类实现,大部分通用的属性都是保存在AbstractBeanDefinition这个类中的。下面查看了一下spring boot的AbstractBeanDefinition,和书中的spring 的差别还是很大的
/**
* Base class for concrete, full-fledged {@link BeanDefinition} classes,
* factoring out common properties of {@link GenericBeanDefinition},
* {@link RootBeanDefinition}, and {@link ChildBeanDefinition}.
*
* <p>The autowire constants match the ones defined in the
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory}
* interface.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Mark Fisher
* @see GenericBeanDefinition
* @see RootBeanDefinition
* @see ChildBeanDefinition
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinition extends BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor
implements BeanDefinition, Cloneable {
/**
* Constant for the default scope name: {@code ""}, equivalent to singleton
* status unless overridden from a parent bean definition (if applicable).
*/
public static final String SCOPE_DEFAULT = "";
/**
* Constant that indicates no autowiring at all.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_NO = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_NO;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by name.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by type.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring a constructor.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR;
/**
* Constant that indicates determining an appropriate autowire strategy
* through introspection of the bean class.
* @see #setAutowireMode
* @deprecated as of Spring 3.0: If you are using mixed autowiring strategies,
* use annotation-based autowiring for clearer demarcation of autowiring needs.
*/
@Deprecated
public static final int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT;
/**
* Constant that indicates no dependency check at all.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE = 0;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for object references.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_OBJECTS = 1;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for "simple" properties.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
* @see org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE = 2;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for all properties
* (object references as well as "simple" properties).
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL = 3;
/**
* Constant that indicates the container should attempt to infer the
* {@link #setDestroyMethodName destroy method name} for a bean as opposed to
* explicit specification of a method name. The value {@value} is specifically
* designed to include characters otherwise illegal in a method name, ensuring
* no possibility of collisions with legitimately named methods having the same
* name.
* <p>Currently, the method names detected during destroy method inference
* are "close" and "shutdown", if present on the specific bean class.
*/
public static final String INFER_METHOD = "(inferred)";
@Nullable
private volatile Object beanClass;
//bean的作用范围,对应bean属性scope
@Nullable
private String scope = SCOPE_DEFAULT;
private boolean abstractFlag = false;
private boolean lazyInit = false;
private int autowireMode = AUTOWIRE_NO;
private int dependencyCheck = DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE;
@Nullable
private String[] dependsOn;
private boolean autowireCandidate = true;
private boolean primary = false;
private final Map<String, AutowireCandidateQualifier> qualifiers = new LinkedHashMap<>(0);
@Nullable
private Supplier<?> instanceSupplier;
private boolean nonPublicAccessAllowed = true;
private boolean lenientConstructorResolution = true;
@Nullable
private String factoryBeanName;
@Nullable
private String factoryMethodName;
@Nullable
private ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArgumentValues;
@Nullable
private MutablePropertyValues propertyValues;
@Nullable
private MethodOverrides methodOverrides;
@Nullable
private String initMethodName;
@Nullable
private String destroyMethodName;
private boolean enforceInitMethod = true;
private boolean enforceDestroyMethod = true;
private boolean synthetic = false;
private int role = BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION;
@Nullable
private String description;
@Nullable
private Resource resource;
/**
* Create a new AbstractBeanDefinition with default settings.
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinition() {
this(null, null);
}
/**
* Create a new AbstractBeanDefinition with the given
* constructor argument values and property values.
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinition(@Nullable ConstructorArgumentValues cargs, @Nullable MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
this.constructorArgumentValues = cargs;
this.propertyValues = pvs;
}
/**
* Create a new AbstractBeanDefinition as a deep copy of the given
* bean definition.
* @param original the original bean definition to copy from
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition original) {
setParentName(original.getParentName());
setBeanClassName(original.getBeanClassName());
setScope(original.getScope());
setAbstract(original.isAbstract());
setLazyInit(original.isLazyInit());
setFactoryBeanName(original.getFactoryBeanName());
setFactoryMethodName(original.getFactoryMethodName());
setRole(original.getRole());
setSource(original.getSource());
copyAttributesFrom(original);
if (original instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
AbstractBeanDefinition originalAbd = (AbstractBeanDefinition) original;
if (originalAbd.hasBeanClass()) {
setBeanClass(originalAbd.getBeanClass());
}
if (originalAbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
setConstructorArgumentValues(new ConstructorArgumentValues(original.getConstructorArgumentValues()));
}
if (originalAbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(original.getPropertyValues()));
}
if (originalAbd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
setMethodOverrides(new MethodOverrides(originalAbd.getMethodOverrides()));
}
setAutowireMode(originalAbd.getAutowireMode());
setDependencyCheck(originalAbd.getDependencyCheck());
setDependsOn(originalAbd.getDependsOn());
setAutowireCandidate(originalAbd.isAutowireCandidate());
setPrimary(originalAbd.isPrimary());
copyQualifiersFrom(originalAbd);
setInstanceSupplier(originalAbd.getInstanceSupplier());
setNonPublicAccessAllowed(originalAbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed());
setLenientConstructorResolution(originalAbd.isLenientConstructorResolution());
setInitMethodName(originalAbd.getInitMethodName());
setEnforceInitMethod(originalAbd.isEnforceInitMethod());
setDestroyMethodName(originalAbd.getDestroyMethodName());
setEnforceDestroyMethod(originalAbd.isEnforceDestroyMethod());
setSynthetic(originalAbd.isSynthetic());
setResource(originalAbd.getResource());
}
else {
setConstructorArgumentValues(new ConstructorArgumentValues(original.getConstructorArgumentValues()));
setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(original.getPropertyValues()));
setResourceDescription(original.getResourceDescription());
}
}
/**
* Override settings in this bean definition (presumably a copied parent
* from a parent-child inheritance relationship) from the given bean
* definition (presumably the child).
* <ul>
* <li>Will override beanClass if specified in the given bean definition.
* <li>Will always take {@code abstract}, {@code scope},
* {@code lazyInit}, {@code autowireMode}, {@code dependencyCheck},
* and {@code dependsOn} from the given bean definition.
* <li>Will add {@code constructorArgumentValues}, {@code propertyValues},
* {@code methodOverrides} from the given bean definition to existing ones.
* <li>Will override {@code factoryBeanName}, {@code factoryMethodName},
* {@code initMethodName}, and {@code destroyMethodName} if specified
* in the given bean definition.
* </ul>
*/
public void overrideFrom(BeanDefinition other) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(other.getBeanClassName())) {
setBeanClassName(other.getBeanClassName());
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(other.getScope())) {
setScope(other.getScope());
}
setAbstract(other.isAbstract());
setLazyInit(other.isLazyInit());
if (StringUtils.hasLength(other.getFactoryBeanName())) {
setFactoryBeanName(other.getFactoryBeanName());
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(other.getFactoryMethodName())) {
setFactoryMethodName(other.getFactoryMethodName());
}
setRole(other.getRole());
setSource(other.getSource());
copyAttributesFrom(other);
if (other instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
AbstractBeanDefinition otherAbd = (AbstractBeanDefinition) other;
if (otherAbd.hasBeanClass()) {
setBeanClass(otherAbd.getBeanClass());
}
if (otherAbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
getConstructorArgumentValues().addArgumentValues(other.getConstructorArgumentValues());
}
if (otherAbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
getPropertyValues().addPropertyValues(other.getPropertyValues());
}
if (otherAbd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
getMethodOverrides().addOverrides(otherAbd.getMethodOverrides());
}
setAutowireMode(otherAbd.getAutowireMode());
setDependencyCheck(otherAbd.getDependencyCheck());
setDependsOn(otherAbd.getDependsOn());
setAutowireCandidate(otherAbd.isAutowireCandidate());
setPrimary(otherAbd.isPrimary());
copyQualifiersFrom(otherAbd);
setInstanceSupplier(otherAbd.getInstanceSupplier());
setNonPublicAccessAllowed(otherAbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed());
setLenientConstructorResolution(otherAbd.isLenientConstructorResolution());
if (otherAbd.getInitMethodName() != null) {
setInitMethodName(otherAbd.getInitMethodName());
setEnforceInitMethod(otherAbd.isEnforceInitMethod());
}
if (otherAbd.getDestroyMethodName() != null) {
setDestroyMethodName(otherAbd.getDestroyMethodName());
setEnforceDestroyMethod(otherAbd.isEnforceDestroyMethod());
}
setSynthetic(otherAbd.isSynthetic());
setResource(otherAbd.getResource());
}
else {
getConstructorArgumentValues().addArgumentValues(other.getConstructorArgumentValues());
getPropertyValues().addPropertyValues(other.getPropertyValues());
setResourceDescription(other.getResourceDescription());
}
}
/**
* Apply the provided default values to this bean.
* @param defaults the defaults to apply
*/
public void applyDefaults(BeanDefinitionDefaults defaults) {
setLazyInit(defaults.isLazyInit());
setAutowireMode(defaults.getAutowireMode());
setDependencyCheck(defaults.getDependencyCheck());
setInitMethodName(defaults.getInitMethodName());
setEnforceInitMethod(false);
setDestroyMethodName(defaults.getDestroyMethodName());
setEnforceDestroyMethod(false);
}
/**
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
*/
@Override
public void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName) {
this.beanClass = beanClassName;
}
/**
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getBeanClassName() {
Object beanClassObject = this.beanClass;
if (beanClassObject instanceof Class) {
return ((Class<?>) beanClassObject).getName();
}
else {
return (String) beanClassObject;
}
}
/**
* Specify the class for this bean.
*/
public void setBeanClass(@Nullable Class<?> beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
}
/**
* Return the class of the wrapped bean, if already resolved.
* @return the bean class, or {@code null} if none defined
* @throws IllegalStateException if the bean definition does not define a bean class,
* or a specified bean class name has not been resolved into an actual Class
*/
public Class<?> getBeanClass() throws IllegalStateException {
Object beanClassObject = this.beanClass;
if (beanClassObject == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No bean class specified on bean definition");
}
if (!(beanClassObject instanceof Class)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Bean class name [" + beanClassObject + "] has not been resolved into an actual Class");
}
return (Class<?>) beanClassObject;
}
/**
* Return whether this definition specifies a bean class.
*/
public boolean hasBeanClass() {
return (this.beanClass instanceof Class);
}
/**
* Determine the class of the wrapped bean, resolving it from a
* specified class name if necessary. Will also reload a specified
* Class from its name when called with the bean class already resolved.
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for resolving a (potential) class name
* @return the resolved bean class
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the class name could be resolved
*/
@Nullable
public Class<?> resolveBeanClass(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String className = getBeanClassName();
if (className == null) {
return null;
}
Class<?> resolvedClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader);
this.beanClass = resolvedClass;
return resolvedClass;
}
/**
* Set the name of the target scope for the bean.
* <p>The default is singleton status, although this is only applied once
* a bean definition becomes active in the containing factory. A bean
* definition may eventually inherit its scope from a parent bean definition.
* For this reason, the default scope name is an empty string (i.e., {@code ""}),
* with singleton status being assumed until a resolved scope is set.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
@Override
public void setScope(@Nullable String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
}
/**
* Return the name of the target scope for the bean.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getScope() {
return this.scope;
}
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single shared instance
* returned from all calls.
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return SCOPE_SINGLETON.equals(scope) || SCOPE_DEFAULT.equals(scope);
}
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
@Override
public boolean isPrototype() {
return SCOPE_PROTOTYPE.equals(scope);
}
/**
* Set if this bean is "abstract", i.e. not meant to be instantiated itself but
* rather just serving as parent for concrete child bean definitions.
* <p>Default is "false". Specify true to tell the bean factory to not try to
* instantiate that particular bean in any case.
*/
public void setAbstract(boolean abstractFlag) {
this.abstractFlag = abstractFlag;
}
/**
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", i.e. not meant to be instantiated
* itself but rather just serving as parent for concrete child bean definitions.
*/
@Override
public boolean isAbstract() {
return this.abstractFlag;
}
/**
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
*/
@Override
public void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit) {
this.lazyInit = lazyInit;
}
/**
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
*/
@Override
public boolean isLazyInit() {
return this.lazyInit;
}
/**
* Set the autowire mode. This determines whether any automagical detection
* and setting of bean references will happen. Default is AUTOWIRE_NO,
* which means there's no autowire.
* @param autowireMode the autowire mode to set.
* Must be one of the constants defined in this class.
* @see #AUTOWIRE_NO
* @see #AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME
* @see #AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE
* @see #AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR
* @see #AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT
*/
public void setAutowireMode(int autowireMode) {
this.autowireMode = autowireMode;
}
/**
* Return the autowire mode as specified in the bean definition.
*/
public int getAutowireMode() {
return this.autowireMode;
}
/**
* Return the resolved autowire code,
* (resolving AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT to AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR or AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE).
* @see #AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT
* @see #AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR
* @see #AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE
*/
public int getResolvedAutowireMode() {
if (this.autowireMode == AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT) {
// Work out whether to apply setter autowiring or constructor autowiring.
// If it has a no-arg constructor it's deemed to be setter autowiring,
// otherwise we'll try constructor autowiring.
Constructor<?>[] constructors = getBeanClass().getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
if (constructor.getParameterCount() == 0) {
return AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE;
}
}
return AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR;
}
else {
return this.autowireMode;
}
}
/**
* Set the dependency check code.
* @param dependencyCheck the code to set.
* Must be one of the four constants defined in this class.
* @see #DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE
* @see #DEPENDENCY_CHECK_OBJECTS
* @see #DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE
* @see #DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL
*/
public void setDependencyCheck(int dependencyCheck) {
this.dependencyCheck = dependencyCheck;
}
/**
* Return the dependency check code.
*/
public int getDependencyCheck() {
return this.dependencyCheck;
}
/**
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
* <p>Note that dependencies are normally expressed through bean properties or
* constructor arguments. This property should just be necessary for other kinds
* of dependencies like statics (*ugh*) or database preparation on startup.
*/
@Override
public void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn) {
this.dependsOn = dependsOn;
}
/**
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] getDependsOn() {
return this.dependsOn;
}
/**
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
* @see #AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE
* @see #AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME
*/
@Override
public void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate) {
this.autowireCandidate = autowireCandidate;
}
/**
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
*/
@Override
public boolean isAutowireCandidate() {
return this.autowireCandidate;
}
/**
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
*/
@Override
public void setPrimary(boolean primary) {
this.primary = primary;
}
/**
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
*/
@Override
public boolean isPrimary() {
return this.primary;
}
/**
* Register a qualifier to be used for autowire candidate resolution,
* keyed by the qualifier's type name.
* @see AutowireCandidateQualifier#getTypeName()
*/
public void addQualifier(AutowireCandidateQualifier qualifier) {
this.qualifiers.put(qualifier.getTypeName(), qualifier);
}
/**
* Return whether this bean has the specified qualifier.
*/
public boolean hasQualifier(String typeName) {
return this.qualifiers.keySet().contains(typeName);
}
/**
* Return the qualifier mapped to the provided type name.
*/
@Nullable
public AutowireCandidateQualifier getQualifier(String typeName) {
return this.qualifiers.get(typeName);
}
/**
* Return all registered qualifiers.
* @return the Set of {@link AutowireCandidateQualifier} objects.
*/
public Set<AutowireCandidateQualifier> getQualifiers() {
return new LinkedHashSet<>(this.qualifiers.values());
}
/**
* Copy the qualifiers from the supplied AbstractBeanDefinition to this bean definition.
* @param source the AbstractBeanDefinition to copy from
*/
public void copyQualifiersFrom(AbstractBeanDefinition source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
this.qualifiers.putAll(source.qualifiers);
}
/**
* Specify a callback for creating an instance of the bean,
* as an alternative to a declaratively specified factory method.
* <p>If such a callback is set, it will override any other constructor
* or factory method metadata. However, bean property population and
* potential annotation-driven injection will still apply as usual.
* @since 5.0
* @see #setConstructorArgumentValues(ConstructorArgumentValues)
* @see #setPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues)
*/
public void setInstanceSupplier(@Nullable Supplier<?> instanceSupplier) {
this.instanceSupplier = instanceSupplier;
}
/**
* Return a callback for creating an instance of the bean, if any.
* @since 5.0
*/
@Nullable
public Supplier<?> getInstanceSupplier() {
return this.instanceSupplier;
}
/**
* Specify whether to allow access to non-public constructors and methods,
* for the case of externalized metadata pointing to those. The default is
* {@code true}; switch this to {@code false} for public access only.
* <p>This applies to constructor resolution, factory method resolution,
* and also init/destroy methods. Bean property accessors have to be public
* in any case and are not affected by this setting.
* <p>Note that annotation-driven configuration will still access non-public
* members as far as they have been annotated. This setting applies to
* externalized metadata in this bean definition only.
*/
public void setNonPublicAccessAllowed(boolean nonPublicAccessAllowed) {
this.nonPublicAccessAllowed = nonPublicAccessAllowed;
}
/**
* Return whether to allow access to non-public constructors and methods.
*/
public boolean isNonPublicAccessAllowed() {
return this.nonPublicAccessAllowed;
}
/**
* Specify whether to resolve constructors in lenient mode ({@code true},
* which is the default) or to switch to strict resolution (throwing an exception
* in case of ambiguous constructors that all match when converting the arguments,
* whereas lenient mode would use the one with the 'closest' type matches).
*/
public void setLenientConstructorResolution(boolean lenientConstructorResolution) {
this.lenientConstructorResolution = lenientConstructorResolution;
}
/**
* Return whether to resolve constructors in lenient mode or in strict mode.
*/
public boolean isLenientConstructorResolution() {
return this.lenientConstructorResolution;
}
/**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
@Override
public void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName) {
this.factoryBeanName = factoryBeanName;
}
/**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getFactoryBeanName() {
return this.factoryBeanName;
}
/**
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
@Override
public void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName) {
this.factoryMethodName = factoryMethodName;
}
/**
* Return a factory method, if any.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getFactoryMethodName() {
return this.factoryMethodName;
}
/**
* Specify constructor argument values for this bean.
*/
public void setConstructorArgumentValues(ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArgumentValues) {
this.constructorArgumentValues = constructorArgumentValues;
}
/**
* Return constructor argument values for this bean (never {@code null}).
*/
@Override
public ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues() {
if (this.constructorArgumentValues == null) {
this.constructorArgumentValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
}
return this.constructorArgumentValues;
}
/**
* Return if there are constructor argument values defined for this bean.
*/
@Override
public boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return (this.constructorArgumentValues != null && !this.constructorArgumentValues.isEmpty());
}
/**
* Specify property values for this bean, if any.
*/
public void setPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.propertyValues = propertyValues;
}
/**
* Return property values for this bean (never {@code null}).
*/
@Override
public MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues() {
if (this.propertyValues == null) {
this.propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
}
return this.propertyValues;
}
/**
* Return if there are property values values defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
@Override
public boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return (this.propertyValues != null && !this.propertyValues.isEmpty());
}
/**
* Specify method overrides for the bean, if any.
*/
public void setMethodOverrides(MethodOverrides methodOverrides) {
this.methodOverrides = methodOverrides;
}
/**
* Return information about methods to be overridden by the IoC
* container. This will be empty if there are no method overrides.
* <p>Never returns {@code null}.
*/
public MethodOverrides getMethodOverrides() {
if (this.methodOverrides == null) {
this.methodOverrides = new MethodOverrides();
}
return this.methodOverrides;
}
/**
* Return if there are method overrides defined for this bean.
* @since 5.0.2
*/
public boolean hasMethodOverrides() {
return (this.methodOverrides != null && !this.methodOverrides.isEmpty());
}
/**
* Set the name of the initializer method.
* <p>The default is {@code null} in which case there is no initializer method.
*/
public void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName) {
this.initMethodName = initMethodName;
}
/**
* Return the name of the initializer method.
*/
@Nullable
public String getInitMethodName() {
return this.initMethodName;
}
/**
* Specify whether or not the configured init method is the default.
* <p>The default value is {@code false}.
* @see #setInitMethodName
*/
public void setEnforceInitMethod(boolean enforceInitMethod) {
this.enforceInitMethod = enforceInitMethod;
}
/**
* Indicate whether the configured init method is the default.
* @see #getInitMethodName()
*/
public boolean isEnforceInitMethod() {
return this.enforceInitMethod;
}
/**
* Set the name of the destroy method.
* <p>The default is {@code null} in which case there is no destroy method.
*/
public void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName) {
this.destroyMethodName = destroyMethodName;
}
/**
* Return the name of the destroy method.
*/
@Nullable
public String getDestroyMethodName() {
return this.destroyMethodName;
}
/**
* Specify whether or not the configured destroy method is the default.
* <p>The default value is {@code false}.
* @see #setDestroyMethodName
*/
public void setEnforceDestroyMethod(boolean enforceDestroyMethod) {
this.enforceDestroyMethod = enforceDestroyMethod;
}
/**
* Indicate whether the configured destroy method is the default.
* @see #getDestroyMethodName
*/
public boolean isEnforceDestroyMethod() {
return this.enforceDestroyMethod;
}
/**
* Set whether this bean definition is 'synthetic', that is, not defined
* by the application itself (for example, an infrastructure bean such
* as a helper for auto-proxying, created through {@code <aop:config>}).
*/
public void setSynthetic(boolean synthetic) {
this.synthetic = synthetic;
}
/**
* Return whether this bean definition is 'synthetic', that is,
* not defined by the application itself.
*/
public boolean isSynthetic() {
return this.synthetic;
}
/**
* Set the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}.
*/
public void setRole(int role) {
this.role = role;
}
/**
* Return the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}.
*/
@Override
public int getRole() {
return this.role;
}
/**
* Set a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
public void setDescription(@Nullable String description) {
this.description = description;
}
/**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getDescription() {
return this.description;
}
/**
* Set the resource that this bean definition came from
* (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
public void setResource(@Nullable Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
/**
* Return the resource that this bean definition came from.
*/
@Nullable
public Resource getResource() {
return this.resource;
}
/**
* Set a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
public void setResourceDescription(@Nullable String resourceDescription) {
this.resource = (resourceDescription != null ? new DescriptiveResource(resourceDescription) : null);
}
/**
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String getResourceDescription() {
return (this.resource != null ? this.resource.getDescription() : null);
}
/**
* Set the originating (e.g. decorated) BeanDefinition, if any.
*/
public void setOriginatingBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition originatingBd) {
this.resource = new BeanDefinitionResource(originatingBd);
}
/**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition() {
return (this.resource instanceof BeanDefinitionResource ?
((BeanDefinitionResource) this.resource).getBeanDefinition() : null);
}
/**
* Validate this bean definition.
* @throws BeanDefinitionValidationException in case of validation failure
*/
public void validate() throws BeanDefinitionValidationException {
if (hasMethodOverrides() && getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException(
"Cannot combine static factory method with method overrides: " +
"the static factory method must create the instance");
}
if (hasBeanClass()) {
prepareMethodOverrides();
}
}
/**
* Validate and prepare the method overrides defined for this bean.
* Checks for existence of a method with the specified name.
* @throws BeanDefinitionValidationException in case of validation failure
*/
public void prepareMethodOverrides() throws BeanDefinitionValidationException {
// Check that lookup methods exists.
if (hasMethodOverrides()) {
Set<MethodOverride> overrides = getMethodOverrides().getOverrides();
synchronized (overrides) {
for (MethodOverride mo : overrides) {
prepareMethodOverride(mo);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Validate and prepare the given method override.
* Checks for existence of a method with the specified name,
* marking it as not overloaded if none found.
* @param mo the MethodOverride object to validate
* @throws BeanDefinitionValidationException in case of validation failure
*/
protected void prepareMethodOverride(MethodOverride mo) throws BeanDefinitionValidationException {
int count = ClassUtils.getMethodCountForName(getBeanClass(), mo.getMethodName());
if (count == 0) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException(
"Invalid method override: no method with name '" + mo.getMethodName() +
"' on class [" + getBeanClassName() + "]");
}
else if (count == 1) {
// Mark override as not overloaded, to avoid the overhead of arg type checking.
mo.setOverloaded(false);
}
}
/**
* Public declaration of Object's {@code clone()} method.
* Delegates to {@link #cloneBeanDefinition()}.
* @see Object#clone()
*/
@Override
public Object clone() {
return cloneBeanDefinition();
}
/**
* Clone this bean definition.
* To be implemented by concrete subclasses.
* @return the cloned bean definition object
*/
public abstract AbstractBeanDefinition cloneBeanDefinition();
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (!(other instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition)) {
return false;
}
AbstractBeanDefinition that = (AbstractBeanDefinition) other;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(getBeanClassName(), that.getBeanClassName())) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.scope, that.scope)) return false;
if (this.abstractFlag != that.abstractFlag) return false;
if (this.lazyInit != that.lazyInit) return false;
if (this.autowireMode != that.autowireMode) return false;
if (this.dependencyCheck != that.dependencyCheck) return false;
if (!Arrays.equals(this.dependsOn, that.dependsOn)) return false;
if (this.autowireCandidate != that.autowireCandidate) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.qualifiers, that.qualifiers)) return false;
if (this.primary != that.primary) return false;
if (this.nonPublicAccessAllowed != that.nonPublicAccessAllowed) return false;
if (this.lenientConstructorResolution != that.lenientConstructorResolution) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.constructorArgumentValues, that.constructorArgumentValues)) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.propertyValues, that.propertyValues)) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.methodOverrides, that.methodOverrides)) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.factoryBeanName, that.factoryBeanName)) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.factoryMethodName, that.factoryMethodName)) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.initMethodName, that.initMethodName)) return false;
if (this.enforceInitMethod != that.enforceInitMethod) return false;
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.destroyMethodName, that.destroyMethodName)) return false;
if (this.enforceDestroyMethod != that.enforceDestroyMethod) return false;
if (this.synthetic != that.synthetic) return false;
if (this.role != that.role) return false;
return super.equals(other);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int hashCode = ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(getBeanClassName());
hashCode = 29 * hashCode + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.scope);
hashCode = 29 * hashCode + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.constructorArgumentValues);
hashCode = 29 * hashCode + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.propertyValues);
hashCode = 29 * hashCode + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.factoryBeanName);
hashCode = 29 * hashCode + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.factoryMethodName);
hashCode = 29 * hashCode + super.hashCode();
return hashCode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("class [");
sb.append(getBeanClassName()).append("]");
sb.append("; scope=").append(this.scope);
sb.append("; abstract=").append(this.abstractFlag);
sb.append("; lazyInit=").append(this.lazyInit);
sb.append("; autowireMode=").append(this.autowireMode);
sb.append("; dependencyCheck=").append(this.dependencyCheck);
sb.append("; autowireCandidate=").append(this.autowireCandidate);
sb.append("; primary=").append(this.primary);
sb.append("; factoryBeanName=").append(this.factoryBeanName);
sb.append("; factoryMethodName=").append(this.factoryMethodName);
sb.append("; initMethodName=").append(this.initMethodName);
sb.append("; destroyMethodName=").append(this.destroyMethodName);
if (this.resource != null) {
sb.append("; defined in ").append(this.resource.getDescription());
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
